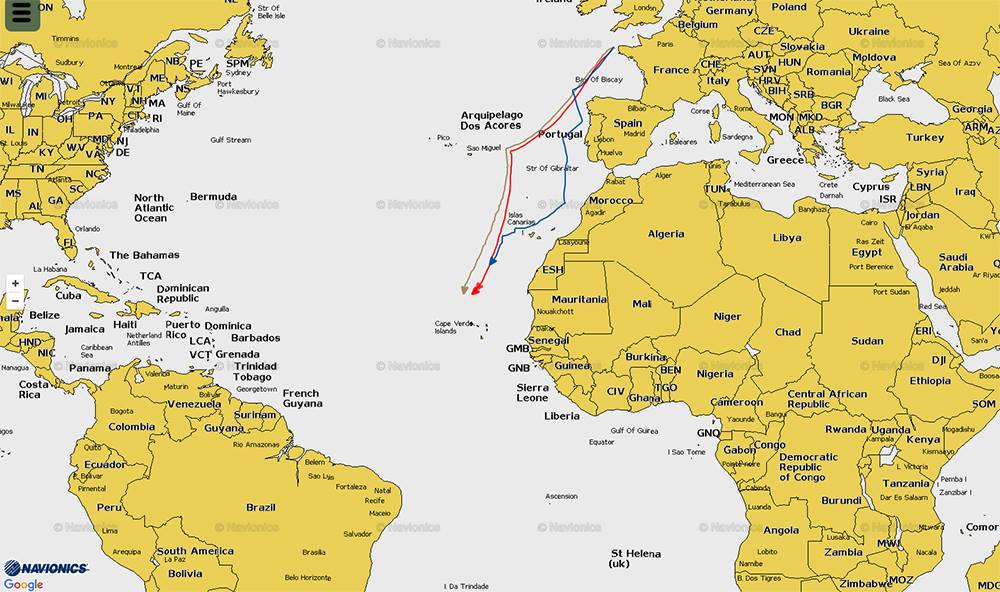
IN 2005-2006 LARRY HUNTINGTON BUILT A 50 FOOT JASON KER DESIGN AT NEB. LAUNCHED FOR THE 2006 BERMUDA RACE IN WHICH WE WON OUR CLASS.
Category: sailing
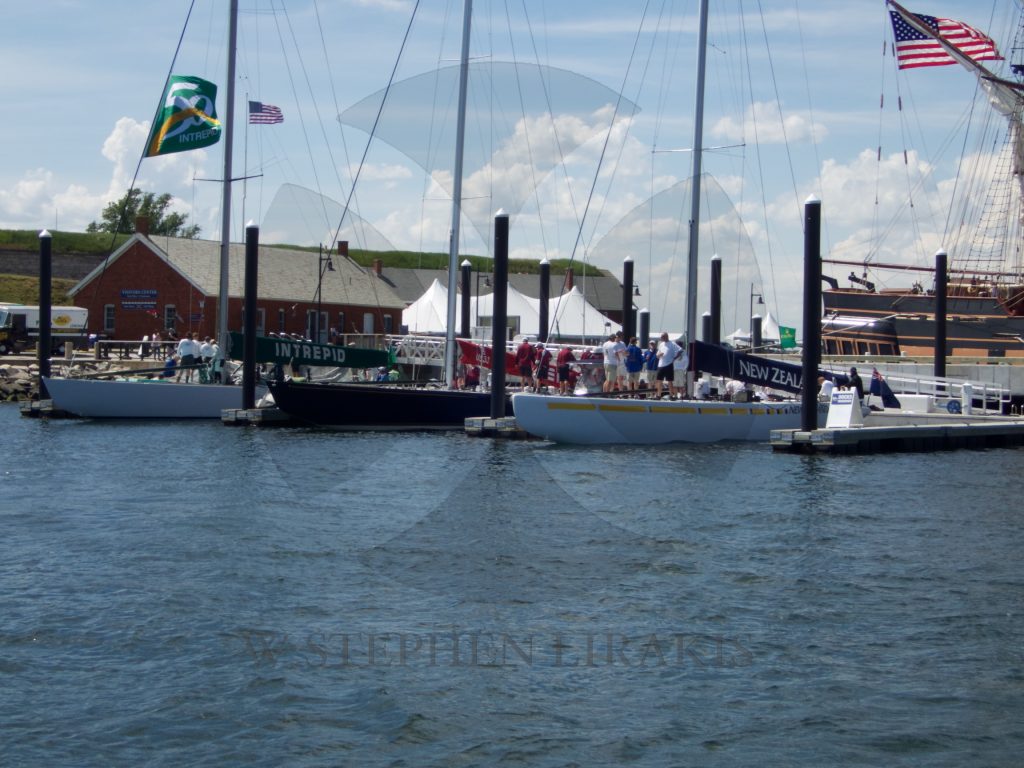
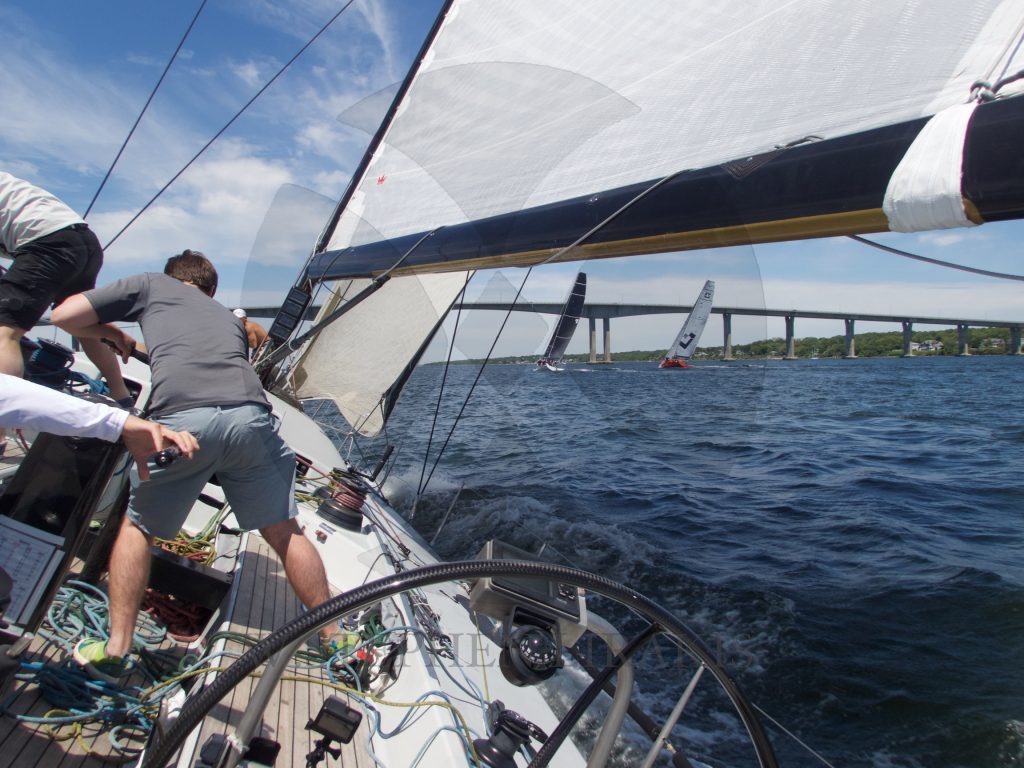
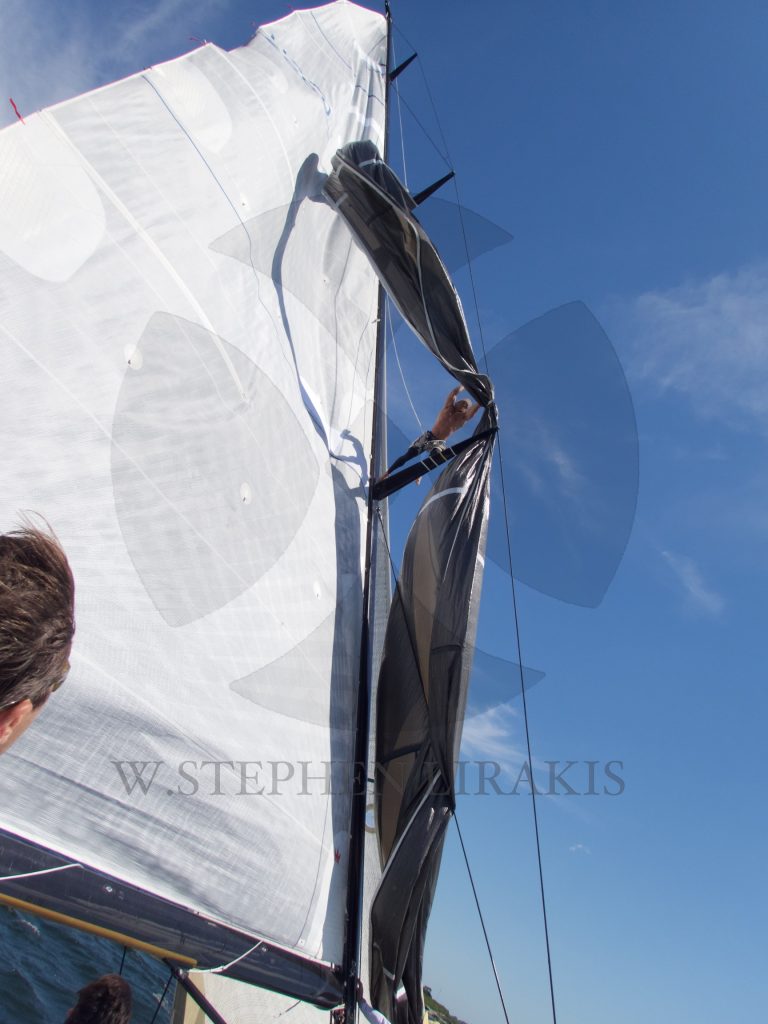
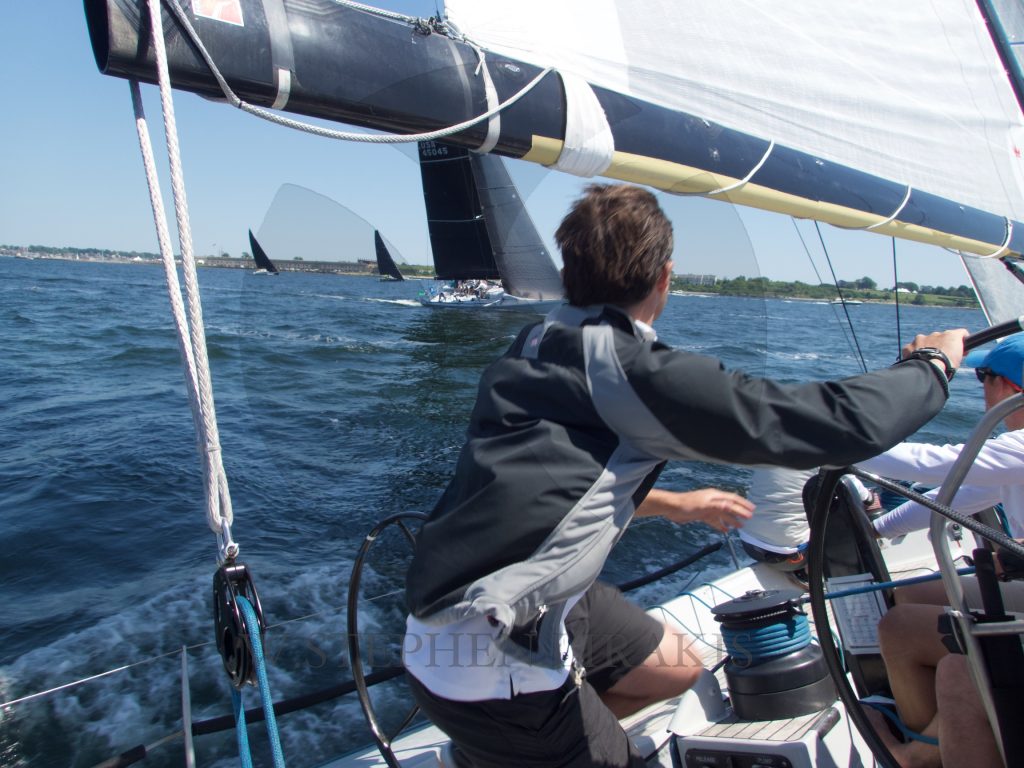
STADIUM SAILING “SIREN”
A WONDERFUL WEEKEND OF CLOSED COURSE SAILING IN NEWPORT RHODE ISALND.
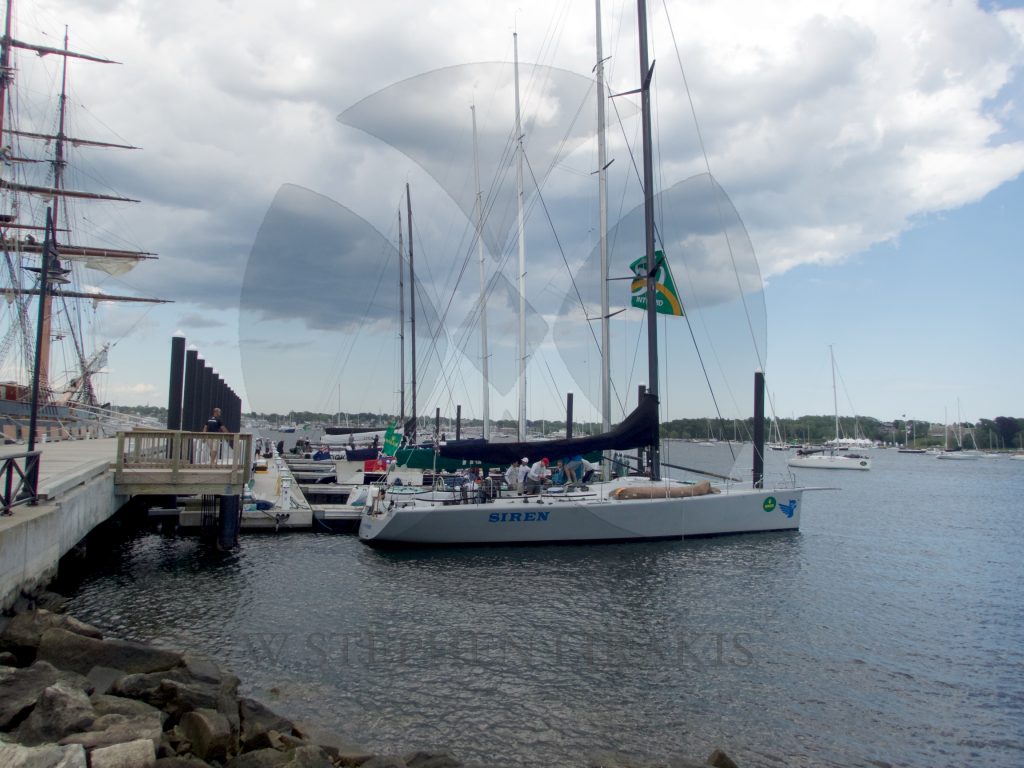





NOTABLE ACHIEVEMENTS
The changes in sailing had been on the horizon for a while. The turning point we can all point to was the last America’s Cup with foiling catamarans.In the Vendee Globe, the boats which have foils are clearly faster.
I believe I read that Joyon cut the jig down on Idec for this attempt; making it an easier boat to handle. Just look at the numbers he is putting up.


CANDY STORE CUP 2016
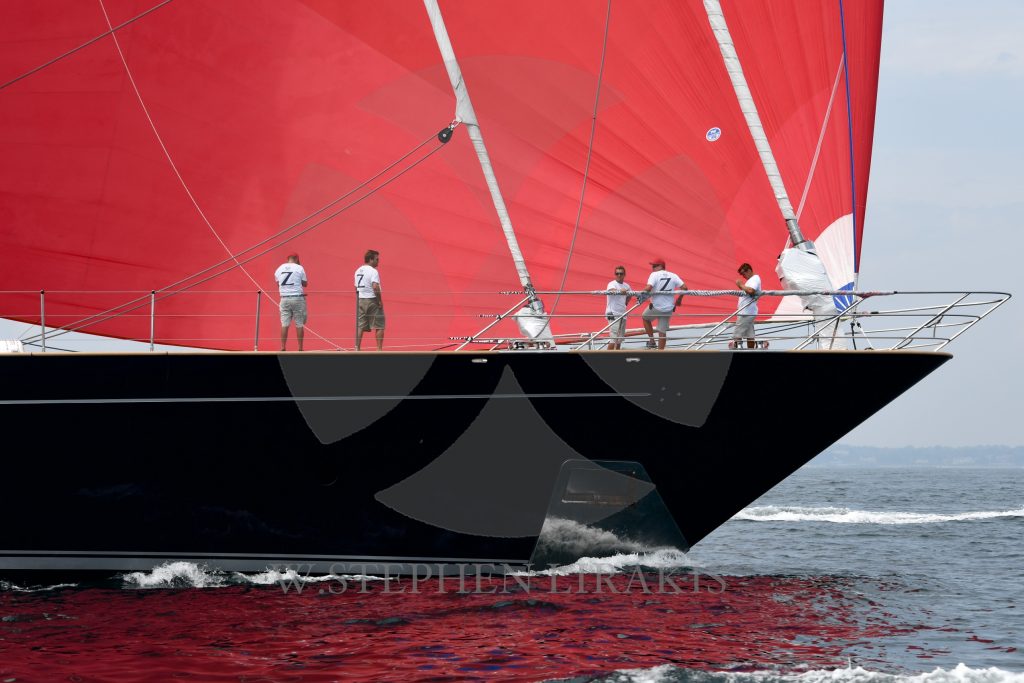
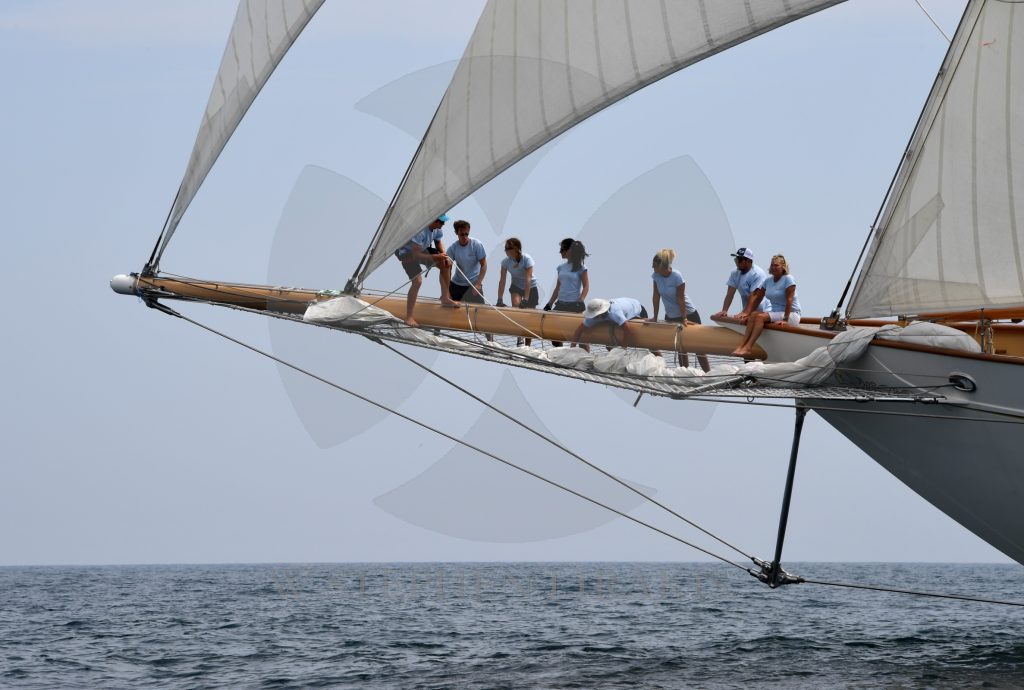
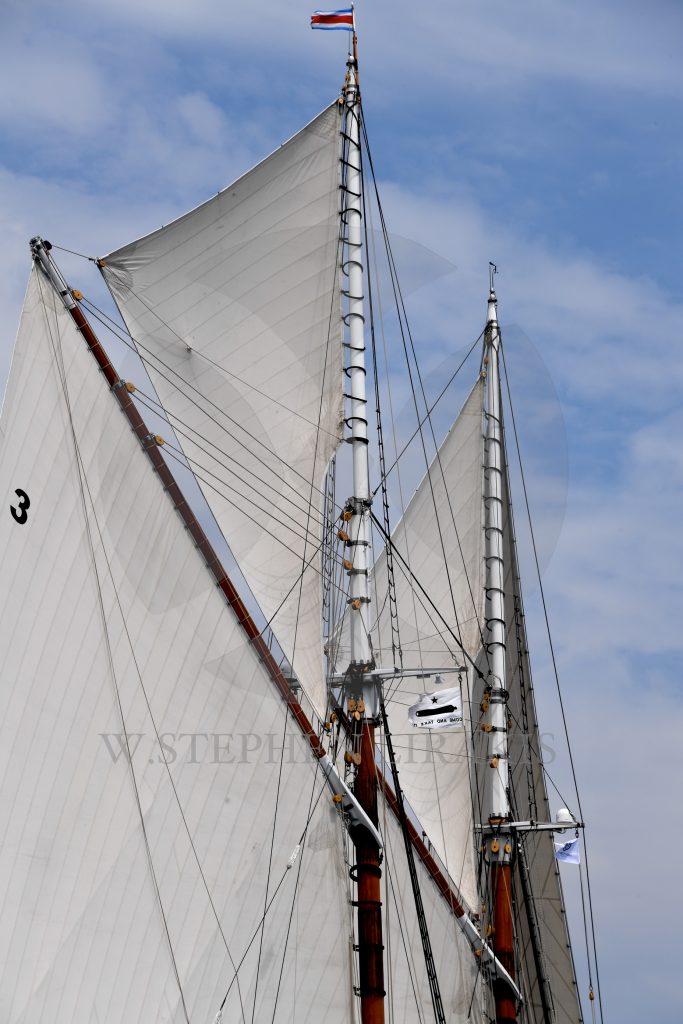
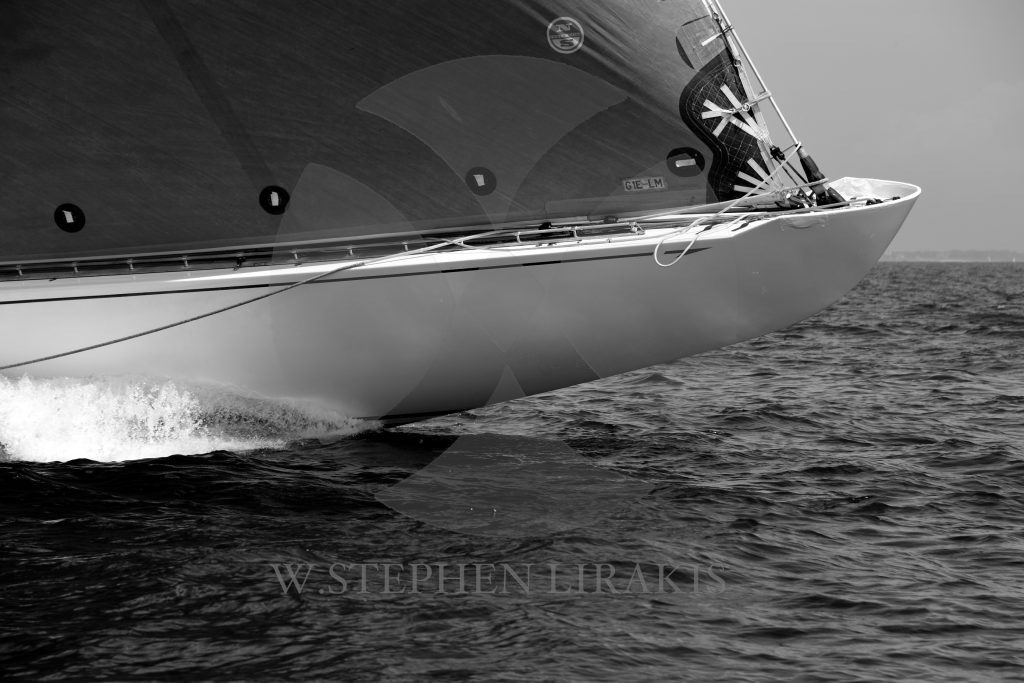
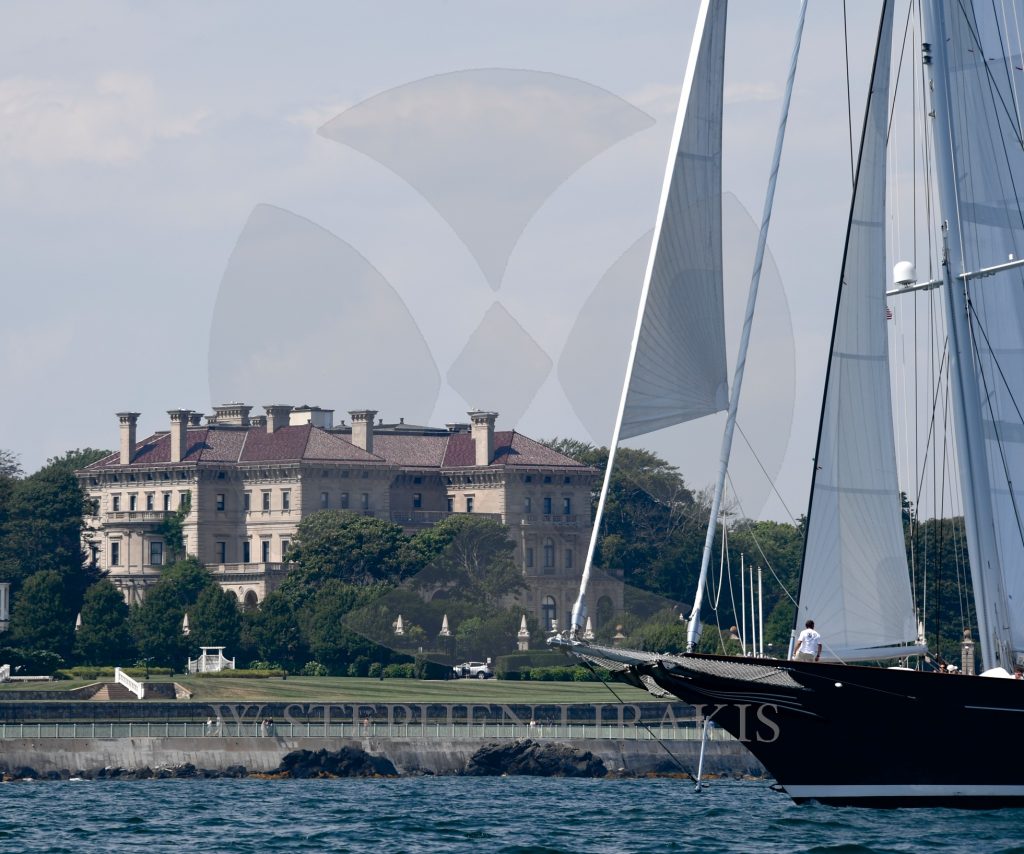
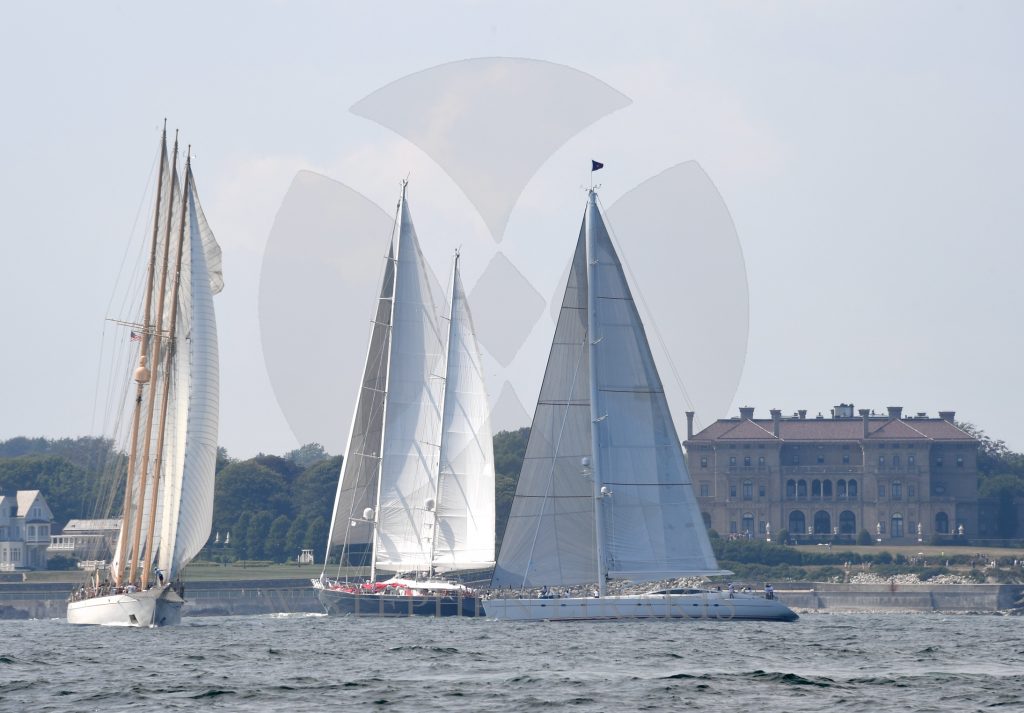
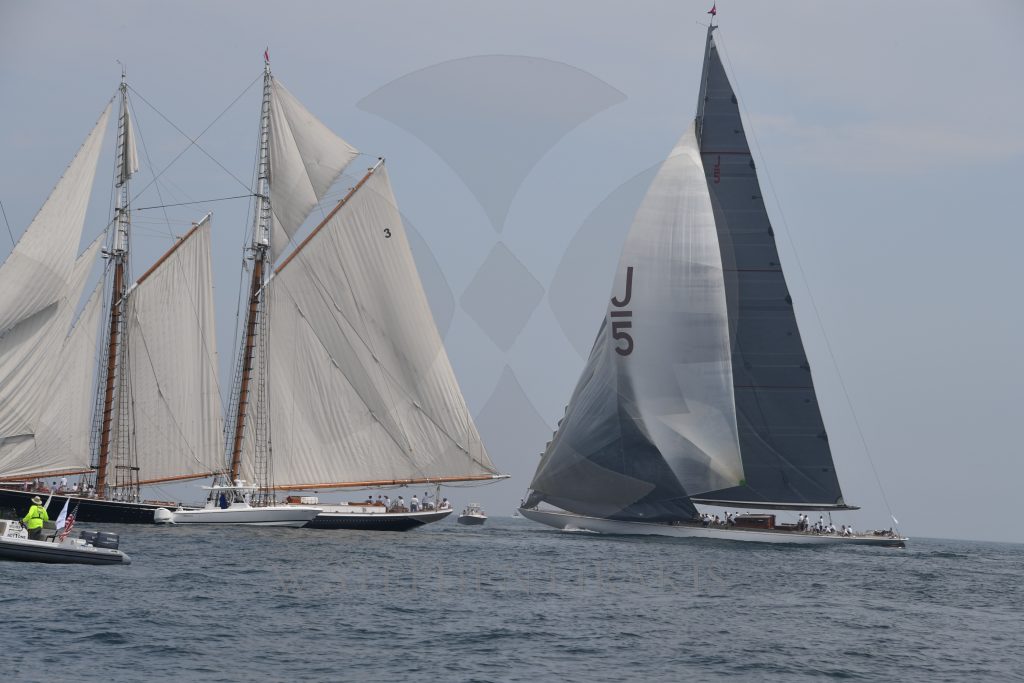







KEEP YOUR KEEL ON
FROM SAILING SCUTTLEBUTT
Keeping Keels Attached in the Future
Published on March 14th, 2016
Stan Honey, chairman of the Oceanic and Offshore Committee at World Sailing, is excited. Too many boats are losing their keels, and he is eager to share some of the progress being made to reverse this trend. Scuttlebutt editor Craig Leweck met with Stan for an update, with additional comments added by Dr. Jason Smithwick, Head of Technical & Offshore at World Sailing.
What are some of the initiatives about how we’re going to keep keels attached?
Stan: The first initiative which has now been approved and budgeted by World Sailing is to have a report writing committee that gets launched to write a report summarizing what happened in any particular incident that World Sailing determines may provide useful information to the sport.
For example, it might provide useful information on ways the Offshore Special Regulations (OSR) could be improved, or may provide useful information in whether the plan review process is working, and whether plan reviewed boats have keels with adequate structure.
The model for that is really the report that Rear Admiral (Rtd) Chris Oxenbould, Chuck Hawley, and myself did for the Vestas Wind grounding during the 2014-15 Volvo Ocean Race. We were asked to write a report and only state on what happened. Our task was not to assign any blame, but just to simply lay out the facts on what occured so that our sport could learn from it.
Of course, what we’re all thinking about is the aviation model. Aviation has more tools to use to encourage information to be made public, but aviation does an astonishingly effective job in how whenever there is a major accident in aviation, there’s always a report that becomes public later. It may be a few years later but there’s always a public report.
Jason: When World Sailing determines a report is needed, we would initiate that report on the basis that no other outside body is already conducting an investigation. For example, if the US Coast Guard is already looking into a loss of life then World Sailing will await the outcome of that report before initiating our own work.
Public reports are a big step.
Stan: The entire industry benefits from this kind of information. As a result of that, in addition to other things, aviation has just achieved a staggering level of safety. Sailing has fewer mechanisms to deal with in terms of the rules and certifications, but, nevertheless, we’re trying to get to the point where when the keel falls off or when there’s a major accident, there’s a report that does not seek to assign blame but rather just to lay out the facts so that people can learn from it.
We will be making a rule change to the OSRs. There’ll probably be a submission at the 2016 World Sailing Annual Conference in November that will put in a requirement as part of the OSRs, that by participating in an event and by holding an event, a competitor and the organizing authority agree to cooperate with the report should an important incident happen and should a report get written.
Sounds like a rule requirement is needed, but also a culture created wherein this kind of information is shared.
Stan: Yes, and it’s the culture that’s the most important one because it’s certainly true that it’s difficult for the rule to be that effective because most rules are designed to influence our behavior during a race, and these are rules that seek to influence our behavior after a race. Many people argue that such a rule is unenforceable and it can’t work. On the other hand, such a rule can help set the culture of the sport in an appropriate direction.
Additionally, such a rule can help owners do what they want to do anyway, which is to help the sport. If an owner is involved in a major incident, they may get encouraged by their builder, their designer, or their insurance company to keep the report private. But this rule would give the owners the ability to say, “No, this is a race boat. I insured it to race and these are the rules of racing, and it says I am to cooperate with a report. That’s what I’m going to do, and that’s the understanding.”
So the rule may not be binding, but it may help to change the culture and it may help the owners to do what they want to do. The insurance companies deny ever encouraging somebody to keep something quiet, as they would. And when you ask the insurance companies about these kinds of changes, they’re hugely supportive. They said, “Hey, wait a minute. Has there been a misunderstanding? We don’t make money when keels fall off.” They’re saying that they’re huge advocates of anything the sport can do to solve the problem of having keels that aren’t adequately attached.
Jason: World Sailing wants to engage the insurance companies within our framework to make plan review more cost efficient. For example, a boat that has had plan review and in-build inspection may have a lower premium to offset the cost of such certification.
Explain the plan review process.
Stan: Yes, we have a plan review process. A plan review is required on any new boat to be built that’s going to race under the OSRs under Categories 0, 1, and 2, although Category 0 frankly isn’t really used. The races that would use the Category 0 basically do their own derivative requirements. Examples of Category 2 is the Fastnet Race and Sydney Hobart.
ABS used to be in the scantlings definition and plan review business some years ago, but they chose to get out of it for smaller recreational boats, so World Sailing now has a new plan review process in partnership with Classification Societies and Notified Bodies which has been a requirement from January 1, 2010.
The most active of the notified bodies that does plan reviews is DNV GL. One of the things that we look at every year is if it is working. Meaning are keels falling off boats where their design had gone to plan review? And the answer prior to two Novembers ago was, “No, it had never happened.” But now the answer is, “Yes, it has happened.” In fact, there were two Class 40s that dropped their keels just before the 2015 Annual Meeting. World Sailing is working with the French authorities to discover the cause of these failures.
So we asked David Lyons, a structural engineer and naval architect, to review the plan review process to determine if it was working. And he confirmed that obviously as people learn more, you change and evolve the plan review process to address new kinds of construction practices and so forth. While he felt that overall the process was working, he pointed out something that’s kind of an obvious omission, which is in almost everything else that humans do.
He found that if something is important enough to be plan reviewed – whether it’s an elevator, an airplane, a building – it’s important enough to do an inspection, an as-built inspection, or an in-build validation is the other term that’s used. David pointed out that this may be something we’d want to consider.
The immediate reaction of our whole community is, “We can’t make this sport any more expensive.” There’s a lot of aspects of the plan review that doesn’t kill people, meaning if a hull comes delaminated, or a deck comes delaminated, or a rig falls over, or a rudder breaks, for the most part, it’s not an instant catastrophe where people die. But when keels fall off, that can be an instant catastrophe leading to immediate loss of life. So what comes to mind is, if we’re going to do an in-build inspection, could we do just one inspection, and can we focus only on the keel attachment since that’s the thing that kills people.
So David’s going to consult across a broad range of the industry experts and look at whether it would be affordable for our sport to extend the plan review process to include an in-build inspection, and as part of a plan review, you’d have to pick when should the inspection take place, at what point in the build, so you can still see what you need to see. As we all know, the beauty of having an inspection process is by nature it can improve things because of the heightened attention by everyone involved.
So the project to come up with a proposal for an in-build inspection if it’s viable, it may not be, turned out to be too big a task to ask David to do as a volunteer. We’re all only human. So we asked for a quotation, and we got a quotation for $40,000 US. For the past month or so I have been trying to raise funds for that.
World Sailing initially committed to fund $10,000 of that. Matt Allen, who is the president of the SOLAS Trust, which is an assistance organization founded by the CYCA following the 1998 Sydney Hobart Race disaster, has offered to cover half of the project – $20,000.
Then RORC and ORC both committed to cover $5,000 of it as well as contribute technical expertise. And both of those organizations have substantial technical expertise in this area, embodied in guys like James Dadd who did this kind of review for the Volvo Ocean Race boats and of course the ITC of the ORC which is a broad strong group of naval architects. Sailing Yacht Research Foundation (SYRF), which is the American sailing and research foundation that also has strong technical people involved like Dina Kowalyshyn and Jim Teeters, has also agreed to pay for $5,000 as well as provide some guidance input.
So overall I was delighted to discover that there was a number of organizations throughout our sport that almost overnight agreed that this was a good idea to consider and agreed to help pay for this initial feasibility study.
Along with the feasibility study there’s a go or no-go decision point. If it looks like it’s feasible and that this will make sense, then there would be a proposal for in-build inspection that will be done by October so we’ll get to review it at the next World Sailing Annual Conference in November.
If it gets approved, we’d probably take another year after that to put it in place, but nevertheless I’m delighted that we’re starting the process to both gather more information about these incidents and get it public where it can do some good, and then also see if we can directly address the problem of these keels falling off.
– See more at: http://www.sailingscuttlebutt.com/2016/03/14/keeping-keels-attached-in-the-future/?utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=Scuttlebutt%204539%20-%20March%2015%202016&utm_content=Scuttlebutt%204539%20-%20March%2015%202016+CID_e7a122f20d7ac7cdc8b3ec3a2b3c3243&utm_source=Email%20Newsletter&utm_term=click%20here#more
DO MORE WITH LESS
I have always had great admiration for those who dare to do.
A smaller boat with a smaller crew require smarter sailing.
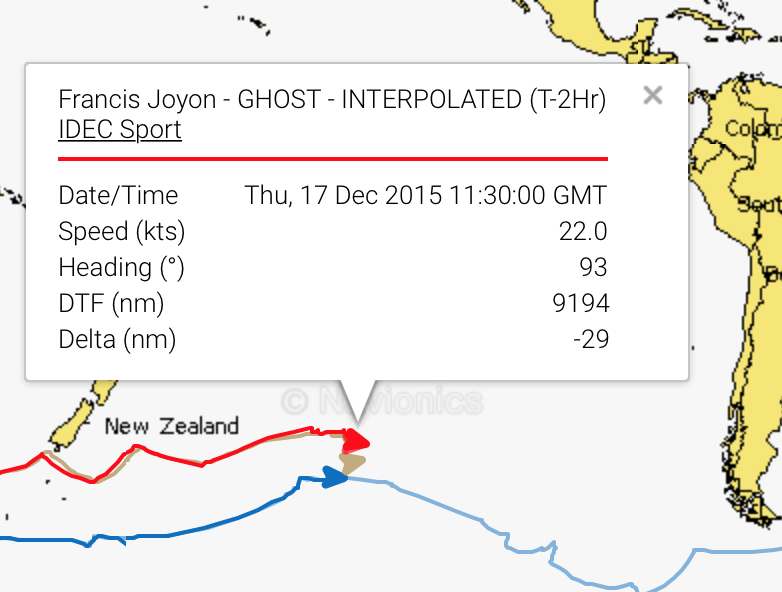
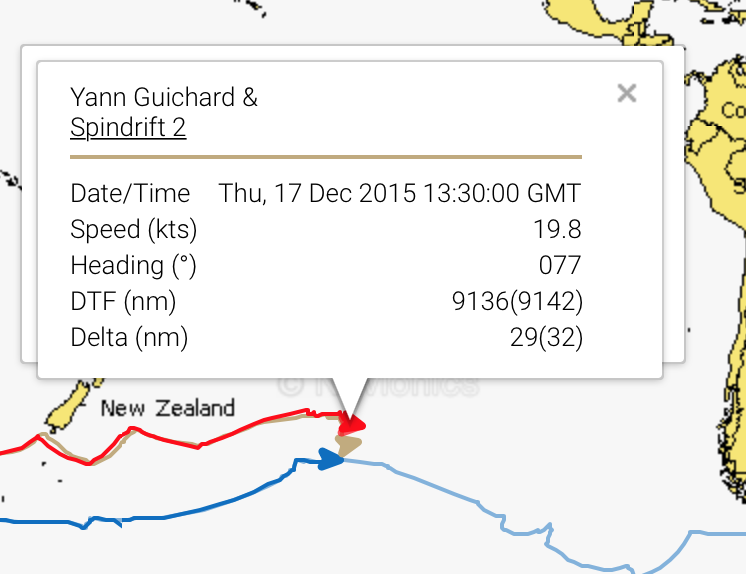
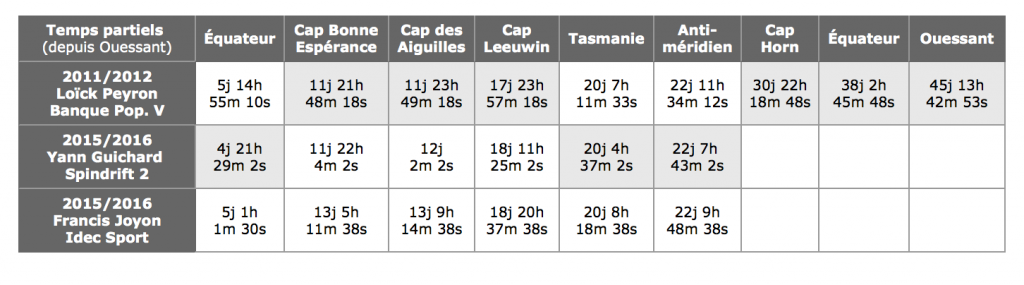
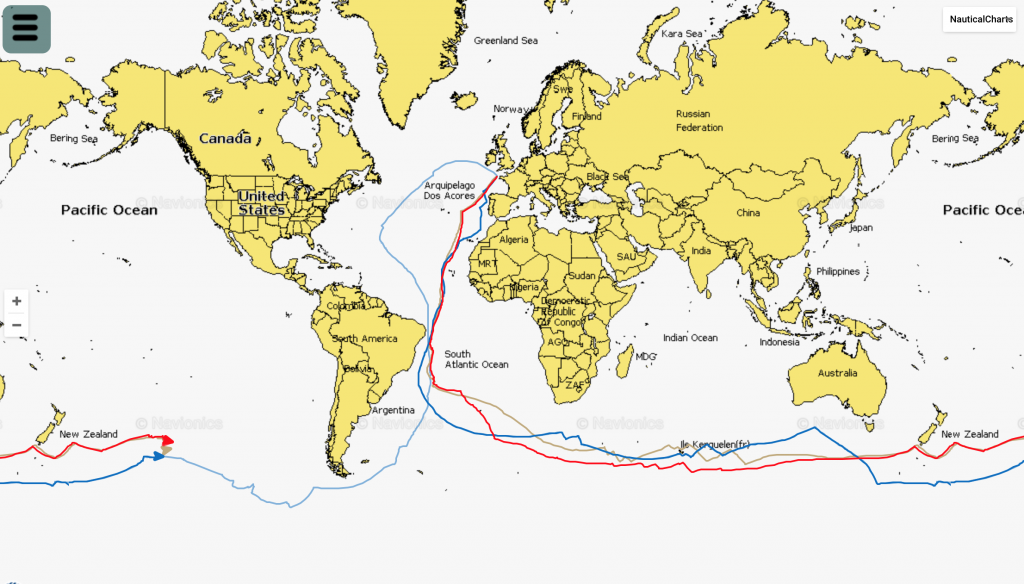
DAY 26 TROPHEE JULES VERNE
BOTH IDEC AND SPINDRIFT ARE CLOSE TO THE “GHOST”. IDEC 30 MILES BEHIND AND SPINDRIFT 30 MILES AHEAD. AT THE SPEEDS THEY ARE SAILING THIS CAN CHANGE VERY QUICKLY. WITH ABOUT 9,000 MILES TO THE FINISH THE DECIDING FACTOR IN THE RACE WILL BE WHO NAVIGATES FROM THE EQUATOR TO THE FINISH WITH THE FASTEST TIME.
JACK LONDON IN A BOAT
|
Small-Boat Sailing
From the Human Drift Collection 1917 |
 A sailor is born, not made. And by “sailor” is meant, not the average efficient and hopeless creature who is found to-day in the forecastle of deepwater ships, but the man who will take a fabric compounded of wood and iron and rope and canvas and compel it to obey his will on the surface of the sea. Barring captains and mates of big ships, the small-boat sailor is the real sailor. He knows—he must know—how to make the wind carry his craft from one given point to another given point. He must know about tides and rips and eddies, bar and channel markings, and day and night signals; he must be wise in weather-lore; and he must be sympathetically familiar with the peculiar qualities of his boat which differentiate it from every other boat that was ever built and rigged. He must know how to gentle her about, as one instance of a myriad, and to fill her on the other tack without deadening her way or allowing her to fall off too far.The deepwater sailor of to-day needs know none of these things. And he doesn’t. He pulls and hauls as he is ordered, swabs decks, washes paint, and chips iron-rust. He knows nothing, and cares less. Put him in a small boat and he is helpless. He will cut an even better figure on the hurricane deck of a horse. A sailor is born, not made. And by “sailor” is meant, not the average efficient and hopeless creature who is found to-day in the forecastle of deepwater ships, but the man who will take a fabric compounded of wood and iron and rope and canvas and compel it to obey his will on the surface of the sea. Barring captains and mates of big ships, the small-boat sailor is the real sailor. He knows—he must know—how to make the wind carry his craft from one given point to another given point. He must know about tides and rips and eddies, bar and channel markings, and day and night signals; he must be wise in weather-lore; and he must be sympathetically familiar with the peculiar qualities of his boat which differentiate it from every other boat that was ever built and rigged. He must know how to gentle her about, as one instance of a myriad, and to fill her on the other tack without deadening her way or allowing her to fall off too far.The deepwater sailor of to-day needs know none of these things. And he doesn’t. He pulls and hauls as he is ordered, swabs decks, washes paint, and chips iron-rust. He knows nothing, and cares less. Put him in a small boat and he is helpless. He will cut an even better figure on the hurricane deck of a horse.
I shall never forget my child-astonishment when I first encountered one of these strange beings. He was a runaway English sailor. I was a lad of twelve, with a decked-over, fourteen-foot, centre-board skiff which I had taught myself to sail. I sat at his feet as at the feet of a god, while he discoursed of strange lands and peoples, deeds of violence, and hair-raising gales at sea. Then, one day, I took him for a sail. With all the trepidation of the veriest little amateur, I hoisted sail and got under way. Here was a man, looking on critically, I was sure, who knew more in one second about boats and the water than I could ever know. After an interval, in which I exceeded myself, he took the tiller and the sheet. I sat on the little thwart amidships, open-mouthed, prepared to learn what real sailing was. My mouth remained open, for I learned what a real sailor was in a small boat. He couldn’t trim the sheet to save himself, he nearly capsized several times in squalls, and, once again, by blunderingly jibing over; he didn’t know what a centre-board was for, nor did he know that in running a boat before the wind one must sit in the middle instead of on the side; and finally, when we came back to the wharf, he ran the skiff in full tilt, shattering her nose and carrying away the mast-step. And yet he was a really truly sailor fresh from the vasty deep. Which points my moral. A man can sail in the forecastles of big ships all his life and never know what real sailing is. From the time I was twelve, I listened to the lure of the sea. When I was fifteen I was captain and owner of an oyster-pirate sloop. By the time I was sixteen I was sailing in scow-schooners, fishing salmon with the Greeks up the Sacramento River, and serving as sailor on the Fish Patrol. And I was a good sailor, too, though all my cruising had been on San Francisco Bay and the rivers tributary to it. I had never been on the ocean in my life. Then, the month I was seventeen, I signed before the mast as an able seaman on a three-top-mast schooner bound on a seven-months’ cruise across the Pacific and back again. As my shipmates promptly informed me, I had had my nerve with me to sign on as able seaman. Yet behold, I WAS an able seaman. I had graduated from the right school. It took no more than minutes to learn the names and uses of the few new ropes. It was simple. I did not do things blindly. As a small-boat sailor I had learned to reason out and know the WHY of everything. It is true, I had to learn how to steer by compass, which took maybe half a minute; but when it came to steering “full-and-by” and “close-and-by,” I could beat the average of my shipmates, because that was the very way I had always sailed. Inside fifteen minutes I could box the compass around and back again. And there was little else to learn during that seven-months’ cruise, except fancy rope-sailorising, such as the more complicated lanyard knots and the making of various kinds of sennit and rope-mats. The point of all of which is that it is by means of small-boat sailing that the real sailor is best schooled. And if a man is a born sailor, and has gone to the school of the sea, never in all his life can he get away from the sea again. The salt of it is in his bones as well as his nostrils, and the sea will call to him until he dies. Of late years, I have found easier ways of earning a living. I have quit the forecastle for keeps, but always I come back to the sea. In my case it is usually San Francisco Bay, than which no lustier, tougher, sheet of water can be found for small-boat sailing. It really blows on San Francisco Bay. During the winter, which is the best cruising season, we have southeasters, southwesters, and occasional howling northers. Throughout the summer we have what we call the “sea-breeze,” an unfailing wind off the Pacific that on most afternoons in the week blows what the Atlantic Coast yachtsmen would name a gale. They are always surprised by the small spread of canvas our yachts carry. Some of them, with schooners they have sailed around the Horn, have looked proudly at their own lofty sticks and huge spreads, then patronisingly and even pityingly at ours. Then, perchance, they have joined in a club cruise from San Francisco to Mare Island. They found the morning run up the Bay delightful. In the afternoon, when the brave west wind ramped across San Pablo Bay and they faced it on the long beat home, things were somewhat different. One by one, like a flight of swallows, our more meagrely sparred and canvassed yachts went by, leaving them wallowing and dead and shortening down in what they called a gale but which we called a dandy sailing breeze. The next time they came out, we would notice their sticks cut down, their booms shortened, and their after-leeches nearer the luffs by whole cloths. As for excitement, there is all the difference in the world between a ship in trouble at sea, and a small boat in trouble on land-locked water. Yet for genuine excitement and thrill, give me the small boat. Things happen so quickly, and there are always so few to do the work–and hard work, too, as the small-boat sailor knows. I have toiled all night, both watches on deck, in a typhoon off the coast of Japan, and been less exhausted than by two hours’ work at reefing down a thirty-foot sloop and heaving up two anchors on a lee shore in a screaming south-easter.
I’ve tried it both ways. I remember labouring in a fourteen days’ gale off the coast of New Zealand. We were a tramp collier, rusty and battered, with six thousand tons of coal in our hold. Life lines were stretched fore and aft; and on our weather side, attached to smokestack guys and rigging, were huge rope-nettings, hung there for the purpose of breaking the force of the seas and so saving our mess-room doors. But the doors were smashed and the mess-rooms washed out just the same. And yet, out of it all, arose but the one feeling, namely, of monotony. In contrast with the foregoing, about the liveliest eight days of my life were spent in a small boat on the west coast of Korea. Never mind why I was thus voyaging up the Yellow Sea during the month of February in below-zero weather. The point is that I was in an open boat, a sampan, on a rocky coast where there were no light-houses and where the tides rip. We did not speak each other’s language. Yet there was nothing monotonous about that trip. Never shall I forget one particular cold bitter dawn, when, in the thick of driving snow, we took in sail and dropped our small anchor. The wind was howling out of the northwest, and we were on a lee shore. Ahead and astern, all escape was cut off by rocky headlands, against whose bases burst the unbroken seas. To windward a short distance, seen only between the snow-squalls, was a low rocky reef. It was this that inadequately protected us from the whole Yellow Sea that thundered in upon us. The Japanese crawled under a communal rice mat and went to sleep. I joined them, and for several hours we dozed fitfully. Then a sea deluged us out with icy water, and we found several inches of snow on top the mat. The reef to windward was disappearing under the rising tide, and moment by moment the seas broke more strongly over the rocks. The fishermen studied the shore anxiously. So did I, and with a sailor’s eye, though I could see little chance for a swimmer to gain that surf-hammered line of rocks. I made signs toward the headlands on either flank. The Japanese shook their heads. I indicated that dreadful lee shore. Still they shook their heads and did nothing. My conclusion was that they were paralysed by the hopelessness of the situation. Yet our extremity increased with every minute, for the rising tide was robbing us of the reef that served as buffer. It soon became a case of swamping at our anchor. Seas were splashing on board in growing volume, and we baled constantly. And still my fishermen crew eyed the surf-battered shore and did nothing. At last, after many narrow escapes from complete swamping, the fishermen got into action. All hands tailed on to the anchor and hove it up. For’ard, as the boat’s head paid off, we set a patch of sail about the size of a flour-sack. And we headed straight for shore. I unlaced my shoes, unbottoned my great-coat and coat, and was ready to make a quick partial strip a minute or so before we struck. But we didn’t strike, and, as we rushed in, I saw the beauty of the situation. Before us opened a narrow channel, frilled at its mouth with breaking seas. Yet, long before, when I had scanned the shore closely, there had been no such channel. I HAD FORGOTTEN THE THIRTY-FOOT TIDE. And it was for this tide that the Japanese had so precariously waited. We ran the frill of breakers, curved into a tiny sheltered bay where the water was scarcely flawed by the gale, and landed on a beach where the salt sea of the last tide lay frozen in long curving lines. And this was one gale of three in the course of those eight days in the sampan. Would it have been beaten on a ship? I fear me the ship would have gone aground on the outlying reef and that its people would have been incontinently and monotonously drowned. There are enough surprises and mishaps in a three-days’ cruise in a small boat to supply a great ship on the ocean for a full year. I remember, once, taking out on her trial trip a little thirty-footer I had just bought. In six days we had two stiff blows, and, in addition, one proper southwester and one ripsnorting southeaster. The slight intervals between these blows were dead calms. Also, in the six days, we were aground three times. Then, too, we tied up to the bank in the Sacramento River, and, grounding by an accident on the steep slope on a falling tide, nearly turned a side somersault down the bank. In a stark calm and heavy tide in the Carquinez Straits, where anchors skate on the channel-scoured bottom, we were sucked against a big dock and smashed and bumped down a quarter of a mile of its length before we could get clear. Two hours afterward, on San Pablo Bay, the wind was piping up and we were reefing down. It is no fun to pick up a skiff adrift in a heavy sea and gale. That was our next task, for our skiff, swamping, parted both towing painters we had bent on. Before we recovered it we had nearly killed ourselves with exhaustion, and we certainly had strained the sloop in every part from keelson to truck. And to cap it all, coming into our home port, beating up the narrowest part of the San Antonio Estuary, we had a shave of inches from collision with a big ship in tow of a tug. I have sailed the ocean in far larger craft a year at a time, in which period occurred no such chapter of moving incident. After all, the mishaps are almost the best part of small-boat sailing. Looking back, they prove to be punctuations of joy. At the time they try your mettle and your vocabulary, and may make you so pessimistic as to believe that God has a grudge against you — but afterward, ah, afterward, with what pleasure you remember them and with what gusto do you relate them to your brother skippers in the fellowhood of small-boat sailing! A narrow, winding slough; a half tide, exposing mud surfaced with gangrenous slime; the water itself filthy and discoloured by the waste from the vats of a near-by tannery; the marsh grass on either side mottled with all the shades of a decaying orchid; a crazy, ramshackled, ancient wharf; and at the end of the wharf a small, white-painted sloop. Nothing romantic about it. No hint of adventure. A splendid pictorial argument against the alleged joys of small-boat sailing. Possibly that is what Cloudesley and I thought, that sombre, leaden morning as we turned out to cook breakfast and wash decks. The latter was my stunt, but one look at the dirty water overside and another at my fresh-painted deck, deterred me. After breakfast, we started a game of chess. The tide continued to fall, and we felt the sloop begin to list. We played on until the chess men began to fall over. The list increased, and we went on deck. Bow-line and stern-line were drawn taut. As we looked the boat listed still farther with an abrupt jerk. The lines were now very taut. “As soon as her belly touches the bottom she will stop,” I said. Cloudesley sounded with a boat-hook along the outside. “Seven feet of water,” he announced. “The bank is almost up and down. The first thing that touches will be her mast when she turns bottom up.” An ominous, minute snapping noise came from the stern-line. Even as we looked, we saw a strand fray and part. Then we jumped. Scarcely had we bent another line between the stern and the wharf, when the original line parted. As we bent another line for’ard, the original one there crackled and parted. After that, it was an inferno of work and excitement. We ran more and more lines, and more and more lines continued to part, and more and more the pretty boat went over on her side. We bent all our spare lines; we unrove sheets and halyards; we used our two-inch hawser; we fastened lines part way up the mast, half way up, and everywhere else. We toiled and sweated and enounced our mutual and sincere conviction that God’s grudge still held against us. Country yokels came down on the wharf and sniggered at us. When Cloudesley let a coil of rope slip down the inclined deck into the vile slime and fished it out with seasick countenance, the yokels sniggered louder and it was all I could do to prevent him from climbing up on the wharf and committing murder. By the time the sloop’s deck was perpendicular, we had unbent the boom-lift from below, made it fast to the wharf, and, with the other end fast nearly to the mast-head, heaved it taut with block and tackle. The lift was of steel wire. We were confident that it could stand the strain, but we doubted the holding-power of the stays that held the mast. The tide had two more hours to ebb (and it was the big run-out), which meant that five hours must elapse ere the returning tide would give us a chance to learn whether or not the sloop would rise to it and right herself. The bank was almost up and down, and at the bottom, directly beneath us, the fast-ebbing tide left a pit of the vilest, illest-smelling, illest-appearing muck to be seen in many a day’s ride. Said Cloudesley to me gazing down into it: “I love you as a brother. I’d fight for you. I’d face roaring lions, and sudden death by field and flood. But just the same, don’t you fall into that.” He shuddered nauseously. “For if you do, I haven’t the grit to pull you out. I simply couldn’t. You’d be awful. The best I could do would be to take a boat-hook and shove you down out of sight.” We sat on the upper side-wall of the cabin, dangled our legs down the top of the cabin, leaned our backs against the deck, and played chess until the rising tide and the block and tackle on the boom-lift enabled us to get her on a respectable keel again. Years afterward, down in the South Seas, on the island of Ysabel, I was caught in a similar predicament. In order to clean her copper, I had careened the Snark broadside on to the beach and outward. When the tide rose, she refused to rise. The water crept in through the scuppers, mounted over the rail, and the level of the ocean slowly crawled up the slant of the deck. We battened down the engine-room hatch, and the sea rose to it and over it and climbed perilously near to the cabin companion-way and skylight. We were all sick with fever, but we turned out in the blazing tropic sun and toiled madly for several hours. We carried our heaviest lines ashore from our mast-heads and heaved with our heaviest purchase until everything crackled including ourselves. We would spell off and lie down like dead men, then get up and heave and crackle again. And in the end, our lower rail five feet under water and the wavelets lapping the companion-way combing, the sturdy little craft shivered and shook herself and pointed her masts once more to the zenith. There is never lack of exercise in small-boat sailing, and the hard work is not only part of the fun of it, but it beats the doctors. San Francisco Bay is no mill pond. It is a large and draughty and variegated piece of water. I remember, one winter evening, trying to enter the mouth of the Sacramento. There was a freshet on the river, the flood tide from the bay had been beaten back into a strong ebb, and the lusty west wind died down with the sun. It was just sunset, and with a fair to middling breeze, dead aft, we stood still in the rapid current. We were squarely in the mouth of the river; but there was no anchorage and we drifted backward, faster and faster, and dropped anchor outside as the last breath of wind left us. The night came on, beautiful and warm and starry. My one companion cooked supper, while on deck I put everything in shape Bristol fashion. When we turned in at nine o’clock the weather-promise was excellent. (If I had carried a barometer I’d have known better.) By two in the morning our shrouds were thrumming in a piping breeze, and I got up and gave her more scope on her hawser. Inside another hour there was no doubt that we were in for a southeaster. It is not nice to leave a warm bed and get out of a bad anchorage in a black blowy night, but we arose to the occasion, put in two reefs, and started to heave up. The winch was old, and the strain of the jumping head sea was too much for it. With the winch out of commission, it was impossible to heave up by hand. We knew, because we tried it and slaughtered our hands. Now a sailor hates to lose an anchor. It is a matter of pride. Of course, we could have buoyed ours and slipped it. Instead, however, I gave her still more hawser, veered her, and dropped the second anchor. There was little sleep after that, for first one and then the other of us would be rolled out of our bunks. The increasing size of the seas told us we were dragging, and when we struck the scoured channel we could tell by the feel of it that our two anchors were fairly skating across. It was a deep channel, the farther edge of it rising steeply like the wall of a canyon, and when our anchors started up that wall they hit in and held. Yet, when we fetched up, through the darkness we could hear the seas breaking on the solid shore astern, and so near was it that we shortened the skiff’s painter. Daylight showed us that between the stern of the skiff and destruction was no more than a score of feet. And how it did blow! There were times, in the gusts, when the wind must have approached a velocity of seventy or eighty miles an hour. But the anchors held, and so nobly that our final anxiety was that the for’ard bitts would be jerked clean out of the boat. All day the sloop alternately ducked her nose under and sat down on her stern; and it was not till late afternoon that the storm broke in one last and worst mad gust. For a full five minutes an absolute dead calm prevailed, and then, with the suddenness of a thunderclap, the wind snorted out of the southwest—a shift of eight points and a boisterous gale. Another night of it was too much for us, and we hove up by hand in a cross head-sea. It was not stiff work. It was heart-breaking. And I know we were both near to crying from the hurt and the exhaustion. And when we did get the first anchor up-and-down we couldn’t break it out. Between seas we snubbed her nose down to it, took plenty of turns, and stood clear as she jumped. Almost everything smashed and parted except the anchor-hold. The chocks were jerked out, the rail torn off, and the very covering-board splintered, and still the anchor held. At last, hoisting the reefed main-sail and slacking off a few of the hard-won feet of the chain, we sailed the anchor out. It was nip and tuck, though, and there were times when the boat was knocked down flat. We repeated the manoeuvre with the remaining anchor, and in the gathering darkness fled into the shelter of the river’s mouth. I was born so long ago that I grew up before the era of gasolene. As a result, I am old-fashioned. I prefer a sail-boat to a motor-boat, and it is my belief that boat-sailing is a finer, more difficult, and sturdier art than running a motor. Gasolene engines are becoming fool-proof, and while it is unfair to say that any fool can run an engine, it is fair to say that almost any one can. Not so, when it comes to sailing a boat. More skill, more intelligence, and a vast deal more training are necessary. It is the finest training in the world for boy and youth and man.If the boy is very small, equip him with a small, comfortable skiff. He will do the rest. He won’t need to be taught. Shortly he will be setting a tiny leg-of-mutton and steering with an oar. Then he will begin to talk keels and centreboards and want to take his blankets out and stop aboard all night. But don’t be afraid for him. He is bound to run risks and encounter accidents. Remember, there are accidents in the nursery as well as out on the water. More boys have died from hot-house culture than have died on boats large and small; and more boys have been made into strong and reliant men by boat-sailing than by lawn-croquet and dancing-school. And once a sailor, always a sailor. The savour of the salt never stales. The sailor never grows so old that he does not care to go back for one more wrestling bout with wind and wave. I know it of myself. I have turned rancher, and live beyond sight of the sea. Yet I can stay away from it only so long. After several months have passed, I begin to grow restless. I find myself day-dreaming over incidents of the last cruise, or wondering if the striped bass are running on Wingo Slough, or eagerly reading the newspapers for reports of the first northern flights of ducks. And then, suddenly, there is a hurried pack of suit-cases and overhauling of gear, and we are off for Vallejo where the little Roamer lies, waiting, always waiting, for the skiff to come alongside, for the lighting of the fire in the galley-stove, for the pulling off of gaskets, the swinging up of the mainsail, and the rat-tat-tat of the reef-points, for the heaving short and the breaking out, and for the twirling of the wheel as she fills away and heads up Bay or down. The Roamer Cruise — related article.
|




 Hard work and excitement? Let the wind baffle and drop in a heavy tide-way just as you are sailing your little sloop through a narrow draw-bridge. Behold your sails, upon which you are depending, flap with sudden emptiness, and then see the impish wind, with a haul of eight points, fill your jib aback with a gusty puff. Around she goes, and sweeps, not through the open draw, but broadside on against the solid piles. Hear the roar of the tide, sucking through the trestle. And hear and see your pretty, fresh-painted boat crash against the piles. Feel her stout little hull give to the impact. See the rail actually pinch in. Hear your canvas tearing, and see the black, square-ended timbers thrusting holes through it. Smash! There goes your topmast stay, and the topmast reels over drunkenly above you. There is a ripping and crunching. If it continues, your starboard shrouds will be torn out. Grab a rope—any rope—and take a turn around a pile. But the free end of the rope is too short. You can’t make it fast, and you hold on and wildly yell for your one companion to get a turn with another and longer rope. Hold on! You hold on till you are purple in the face, till it seems your arms are dragging out of their sockets, till the blood bursts from the ends of your fingers. But you hold, and your partner gets the longer rope and makes it fast. You straighten up and look at your hands. They are ruined. You can scarcely relax the crooks of the fingers. The pain is sickening. But there is no time. The skiff, which is always perverse, is pounding against the barnacles on the piles which threaten to scrape its gunwale off. It’s drop the peak! Down jib! Then you run lines, and pull and haul and heave, and exchange unpleasant remarks with the bridge-tender who is always willing to meet you more than half way in such repartee. And finally, at the end of an hour, with aching back, sweat-soaked shirt, and slaughtered hands, you are through and swinging along on the placid, beneficent tide between narrow banks where the cattle stand knee-deep and gaze wonderingly at you. Excitement! Work! Can you beat it in a calm day on the deep sea?
Hard work and excitement? Let the wind baffle and drop in a heavy tide-way just as you are sailing your little sloop through a narrow draw-bridge. Behold your sails, upon which you are depending, flap with sudden emptiness, and then see the impish wind, with a haul of eight points, fill your jib aback with a gusty puff. Around she goes, and sweeps, not through the open draw, but broadside on against the solid piles. Hear the roar of the tide, sucking through the trestle. And hear and see your pretty, fresh-painted boat crash against the piles. Feel her stout little hull give to the impact. See the rail actually pinch in. Hear your canvas tearing, and see the black, square-ended timbers thrusting holes through it. Smash! There goes your topmast stay, and the topmast reels over drunkenly above you. There is a ripping and crunching. If it continues, your starboard shrouds will be torn out. Grab a rope—any rope—and take a turn around a pile. But the free end of the rope is too short. You can’t make it fast, and you hold on and wildly yell for your one companion to get a turn with another and longer rope. Hold on! You hold on till you are purple in the face, till it seems your arms are dragging out of their sockets, till the blood bursts from the ends of your fingers. But you hold, and your partner gets the longer rope and makes it fast. You straighten up and look at your hands. They are ruined. You can scarcely relax the crooks of the fingers. The pain is sickening. But there is no time. The skiff, which is always perverse, is pounding against the barnacles on the piles which threaten to scrape its gunwale off. It’s drop the peak! Down jib! Then you run lines, and pull and haul and heave, and exchange unpleasant remarks with the bridge-tender who is always willing to meet you more than half way in such repartee. And finally, at the end of an hour, with aching back, sweat-soaked shirt, and slaughtered hands, you are through and swinging along on the placid, beneficent tide between narrow banks where the cattle stand knee-deep and gaze wonderingly at you. Excitement! Work! Can you beat it in a calm day on the deep sea?